Effective Web page testing
The short answer: All testing is risk-based; we cannot test everything. So we make educated assumptions. Certain fields may contain data which is not persisted in the database -- these fields might be lower-risk and perhaps do not need as much testing as others. Or the developer who coded the form may be poorly familiar with field validation and you may need to test more.
The long answer? Yes, each and every field should be tested. It is the challenge of a tester to rise to the occasion and develop methodologies and tools which make him or her more efficient and more effective. Through the use of automation, it may be possible to test each field for boundary and equivalence class partitions. Perhaps by writing code which creates the HTTP POST or GET, rather than filling in each form, this coverage can be obtained. Or using data-driven testing and Selenium or Watij (Watin, Watir, etc.) it might be possible to automated the form once and loop through a series (or generate a series of data programmatically) to test boundaries and equivalence classes. Also, making use of PICT tools (pairwise, interdependent, combinatorial testing) can help you use science to narrow the field of tests you need to run to gain adequate coverage.
The key to rising above other testers and QA engineers is to tackle these challenges head-on. There are many who think testers are just developers who "couldn't cut it" as developers. Unfortunately, in some cases, this is true. But the true tester will take these complicated challenges and rise above them, and will come up with creative ways to apply their engineering skills to accomplish the work at hand. And even when it's not possible to test everything, a good tester will know through logic, experience, and science when testing is complete.
So the full answer is simple, but not easy. Be smart and make use of any and all tools around you. Figure out what you can accomplish in the time given, and get to it. Be scientific and think through the problem, and leverage technology to implement the solution. The goal is to have tested as much as possible in the time provided, and you will be amazed what you can do if you just take some time to figure it out.
Like the guide, then subscribe by entering you mail id to get updates daily
Don't miss any article:Get it by E-mail
Software performance testing: There is no 'I' in 'team'
It makes more sense to think about performance testing and tuning as a team sport in which the following takes place:
- The team works together collaboratively
- The team is informed and involved in the decision-making process about what to test next
- The team generates ideas about how the performance tester can help isolate performance issues using the tools that are exclusively available to him
- The team finds out about performance issues in real time
- The team gets to work together to help find functional errors under load
- The members of the team who best understand the various components of the system under test get to participate in analyzing the results data in real time
- The performance tester gets to sit next to the developer during the tune-retest-retune-retest cycle (frequently shortening that cycle from days or weeks to hours)
Maybe I should rethink my conference
When everyone on the team does his job and works together to support one another the net result is almost always dramatically more desirable.
Like the guide, then subscribe by entering you mail id to get updates dailyDon't miss any article:Get it by E-mail
Living life as a Software Tester!
I will extract only points related to software testing. As a software tester keep in mind these simple points:
Share everything:
If you are a experienced tester on any project then help the new developers on your project. Some testers have habit to keep the known bugs hidden till they get implement in code and then they write a big defect report on that. Don’t try to only pump your bug count, share everything with developers.
Build trust:
Let the developers know any bug you found in design phase. Do not log the bug repeatedly with small variations just to pump the bug count. Build trust in developer and tester relation.
Don’t blame others:As a tester you should not always blame developers for the bugs. Concentrate on bug, not always on pointing that bug in front of all people. Hit the bug and its cause not the developer!
Clean up your own mess:
When you finish doing any test scenario then reconfigure that machine to its original configuration. The same case applies for bug report. Write a clean effective bug report. Let the developer find it easy to repro and fix it.
Give credit to others for their work:
Do not take others credit. If you have referred any others work, immediately give credit to that person. Do not get frustrated if you not found any bug that later has been reported by client. Do work hard, use your skill.
Remember to flush Like the toilets flush all the software’s at some point. While doing performance testing remember to flush the system cache.
Take a nap everyday:
We need time to think, get refresh or to regenerate our energy.Some times its important to take one step back in order to get fresh insight and to find different working approach.
Always work in teams, team score are always better and powerful than individuals.
Like the guide, then subscribe by entering you mail id to get updates daily
Don't miss any article:Get it by E-mail
Testing Metrics - Do you have examples?
| Possible testing metrics are here: • Number of test cases |
| • Number of tests executed |
| • Number of tests passed |
| • Number of tests failed |
| • Number of re-tests |
| • Number of Requirements tested |
| • Number of Defects per lines of software code or per function |
| • Number of Defects found in computer file types (e.g. jav, aspx, xml, xslt, html, com, doc) |
Like the guide, then subscribe by entering you mail id to get updates daily
Don't miss any article:Get it by E-mail
What are the 10 best steps for software testing?
| Here are the top 10 steps to follow while doing software testing 1. Establish the Test Methodology you wish to follow ... E.g. ISEB |
| 2. Establish the Test Principle ... E.g. Fail fast |
| 3. Define the Requirements ... If there are no requirements then there is nothing to test |
| 4. Document the Requirements Traceability matrix ... This should work in both directions |
| 5. Define the specific tests which apply in your situation |
| 6. Document the test plan |
| 7. Document the test cases |
| 8. Define the start of testing |
| 9. Conduct testing |
| 10. Define the point at which testing can stop ... When the benefit of continuing testing is outweighed by the effort of continuing testing |
Like the guide, then subscribe by entering you mail id to get updates daily
Don't miss any article:Get it by E-mail
133 Software Testing Interview Questions
If you know the answers please post your ans along with the question number.
Ofcourse am giving links to some of the questions to find the correct answer.
Do post your answers and help the people in finding answers.
And also do mention your mail id in comment to get the answers for all the 133 Questions.
Best of luck..!!
- What is Software Testing?
- What is the Purpose of Testing?
- What types of testing do testers perform?
- What is the Outcome of Testing?
- What kind of testing have you done?
- What is the need for testing?
- What are the entry criteria for Functionality and Performance testing?
- What is test metrics?
- Why do you go for White box testing, when Black box testing is available?
- What are the entry criteria for Automation testing?
- When to start and Stop Testing?
- What is Quality?
- What is Baseline document, Can you say any two?
- What is verification?
- What is validation?
- What is quality assurance?
- What is quality control?
- What is SDLC and TDLC?
- What are the Qualities of a Tester?
- When to start and Stop Testing?
- What are the various levels of testing?
- What are the types of testing you know and you experienced?
- What exactly is Heuristic checklist approach for unit testing?
- After completing testing, what would you deliver to the client?
- What is a Test Bed?
- What is a Data Guidelines?
- Why do you go for Test Bed?
- What is Severity and Priority and who will decide what?
- Can Automation testing replace manual testing? If it so, how?
- What is a test case?
- What is a test condition?
- What is the test script?
- What is the test data?
- What is an Inconsistent bug?
- What is the difference between Re-testing and Regression testing?
- What are the different types of testing techniques?
- What are the different types of test case techniques?
- What are the risks involved in testing?
- Differentiate Test bed and Test Environment?
- What ifs the difference between defect, error, bug, failure, fault?
- What is the difference between quality and testing?
- What is the difference between White & Black Box Testing?
- What is the difference between Quality Assurance and Quality Control?
- What is the difference between Testing and debugging?
- What is the difference between bug and defect?
- What is the difference between verification and validation?
- What is the difference between functional spec. and Business requirement specification?
- What is the difference between unit testing and integration testing?
- What is the diff between Volume & Load?
- What is diff between Volume & Stress?
- What is the diff between Stress & Load Testing?
- What is the Diff between Two Tier & Three tier Architecture?
- What is the diff between Client Server & Web Based Testing?
- What is the diff between Integration & System Testing?
- What is the Diff between Code Walkthrough & Code Review?
- What is the diff between walkthrough and inspection?
- What is the Diff between SIT & IST?
- What is the Diff between static and dynamic?
- What is the diff between alpha testing and beta testing?
- What are the Minimum requirements to start testing?
- What is Smoke Testing & when it will be done?
- What is Adhoc Testing? When it can be done?
- What is cookie testing?
- What is security testing?
- What is database testing?
- What is the relation ship between Quality & Testing?
- How do you determine, what to be tested?
- How do you go about testing a project?
- What is the Initial Stage of testing?
- What is Web Based Application Testing?
- What is Client Server Application Testing?
- What is Two Tier & Three tier Architecture?
- What is the use of Functional Specification?
- Why do we prepare test condition, test cases, test script (Before Starting Testing)?
- Is it not waste of time in preparing the test condition, test case & Test Script?
- How do you go about testing of Web Application?
- How do you go about testing of Client Server Application?
- What is meant by Static Testing?
- Can the static testing be done for both Web & Client Server Application?
- In the Static Testing, what all can be tested?
- Can test condition, test case & test script help you in performing the static testing?
- What is meant by dynamic testing?
- Is the dynamic testing a functional testing?
- Is the Static testing a functional testing?
- What are the functional testing you perform?
- What is meant by Alpha Testing?
- What kind of Document you need for going for an Functional testing?
- What is meant by Beta Testing?
- At what stage the unit testing has to be done?
- Who can perform the Unit Testing?
- When will the Verification & Validation be done?
- What is meant by Code Walkthrough?
- What is meant Code Review?
- What is the testing that a tester performs at the end of Unit Testing?
- What are the things, you prefer & Prepare before starting Testing?
- What is Integration Testing?
- What is Incremental Integration Testing?
- What is meant by System Testing?
- What is meant by SIT?
- When do you go for Integration Testing?
- Can the System testing be done at any stage?
- What are stubs & drivers?
- What is the Concept of Up-Down & Down-Up in Testing in integration testing?
- What is the final Stage of Integration Testing?
- Where in the SDLC, the Testing Starts?
- What is the Outcome of Integration Testing?
- What is meant by GUI Testing?
- What is meant by Back-End Testing?
- What are the features, you take care in Prototype testing?
- What is Mutation testing & when can it be done?
- What is Compatibility Testing?
- What is Usability Testing?
- What is the Importance of testing?
- What is meant by regression Testing?
- When we prefer Regression & what are the stages where we go for Regression Testing?
- What is performance testing?
- What is the Performance testing; those can be done Manually & Automatically?
- What is Volume, Stress & Load Testing?
- What is a Bug?
- What is a Defect?
- What is the defect Life Cycle?
- What is the Priority in fixing the Bugs?
- Explain the Severity you rate for the bugs found?
- Diff between UAT & IST?
- What is meant by UAT?
- What all are the requirements needed for UAT?
- What are the docs required for Performance Testing?
- What is risk analysis?
- How to do risk management?130. What are test closure documents?
- What is traceability matrix?
- What ways you followed for defect management?and finally
- What is diff betn Smoke Testing and Sanity Testing?
- What is the though situation you ever faced in testing?
Don't miss any article:Get it by E-mail
Finding and Logging a Bug-A good video from Sara Ford
Like the guide, then subscribe by entering you mail id to get updates daily
Topics to learn before attending interview
Anyway i will try to list important and most real time using things:
- Testing Terminology
- SDLC Models
- Test Life cycle(STLC)
- V-Model for testing
- Defect Life cycle
- Test case Preparation
- a. Functional Test Case Preparation
- b. GUI Test Case Preparation
- Test Data Preparation
- Test case Review
- Test Case Execution
- Smoke/Sanity Testing
- Retesting ,Regression Testing Process
- Bug/Defect Report writing
- Bug or Defect Reporting and Tracking
- Test summary Report Preparation
- Excel using skills
The above mentioned things are minimum that you should learn to survive in software testing profession.Please try to learn atlest above things before going to any testing interview.
Like the guide, then subscribe by entering you mail id to get updates dailyDon't miss any article:Get it by E-mail
Software Testing Certification Programs
If you are in software field, you might have heard about java certified boy or oracle certified girl. Basically these are exams which are specific to a software discipline conducted by some institutes.When you pass the exam with or without flying colors you become certified in that discipline.
Why should I be certified or what are the advantages of getting certified?
Well most of these institutes are international bodies, so when you get certified in a discipline, its a formal recognition that you have demonstrated a certain level of competence in the corresponding discipline
Advantages:
'Exam',the one word that forced us to open even the most boring books and made us go through them all night as if they were J.K Rowling Novels.Well here, by volunteering yourself to take the exam and by paying large sums of money, you force yourself to gain knowledge in the corresponding discipline.
You will get Recognized by your peers and most importantly your boss.Management respects those who put forth the personal effort needed for self-improvement. The rewards may come in the form of promotions, increased pay.Adds color to your resume.
Are there any certifications for software testing?
Yup,the following are some of the certification programs for software testing
- Certified Software Tester (CSTE): This certification mostly tests the knowledge of the software testing concepts, principles and practices
- Advanced Software Tester (ASTE):This certification tests the ability to develop real solutions to software testing challenges in the current IT organizations, by proposing a solution to a real-world problem.
- Master Software Tester (MSTE):This certification tests the ability to innovate beyond current testing practices insolving IT challenges, as well as, demonstrate public service in the IT testingprofession.
How can I get certified?
Cool dude's four steps for getting certified
Step1: Apply for the exam - fill some applications, pay some money
Step2: Study for 3 months - For 2 months and 3 weeks 'we can always postpone'.Last week, study very seriously
Step3: Write the exam
Step4: Get passing gradesCongratulations! you are certified.
For more informaton on where can I get the applicaton form, how much money I should spend etc., visit the site softwarecertifications
Like the guide, then subscribe by entering you mail id to get updates dailyDon't miss any article:Get it by E-mail
Software Testing Challenges
- Training in testing
- Relationship building with developers
- Using tools
- Getting managers to understand testing
- Communicating with users about testing
- Making the necessary time for testing
- Testing “over the wall” software
- Trying to hit a moving target
- Fighting a lose-lose situation
- Having to say “no”
Like the guide, then subscribe by entering you mail id to get updates daily
Don't miss any article:Get it by E-mail
VMWare - A Tester's Best Friend-1
The most important part of VMImage is adding additional memory or hard disk or even CPU. You add these resources only when the Image is shutdown. This can be done from the VM settings.
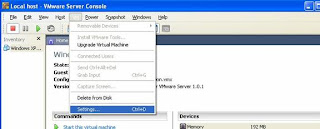
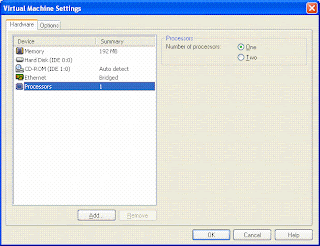
Snapshots:
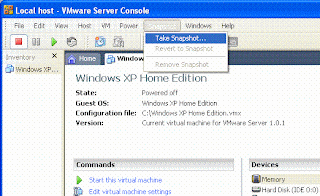
A snapshot is a frozen image of your virtual OS at any particular point of time. This feature is very useful for backups. In my case, when I had setup the entire Japanese Environment by installing the SQL Server 2005 Japanese and Sun Java System Application server 9.1 Multi language. The application was up and running I created a snapshot for this. Snapshots enable a tester to return to last stable environment if anything goes awry. You can create snapshots only when the Vmimage is Powered Off. The snapshot created is saved in the same folder as your VMImage. You can just revert to snapshot if your setting gets corrupted. This saves time of the testers of uninstalling and installing or setting the corrupted environment right.
Once a VMImage is created it is a ‘Reusable Asset’. I had Created a Japanese VMImage and used the same for different databases. The Environment can be replicated by just copying the VMImage from one machine to another. Copy a VMImage from one machine to another. When you will power on this VMImage it will give a message that the Image is being copied so do you want to create a new identifier. Just say yes. Now this VMImage works fine on any machine. The same environment can be replicated on any number of machines simply by copying, which otherwise would have taken hours or even days.
Hope this will help you in using VMImages and improve your productivity.
Don't miss any article:Get it by E-mail
VMWare - A Tester's Best Friend
- Different OS Platforms
- Different Browsers.
- Different Databases
- Different Application servers
The requirement of different hardware resources is directly proportional to the complexity of the configuration matrix. This causes a pain in the neck of software testers as they will have to invest most of their time in setting up different environments. ‘VIRTUALISATION’ can help you rise to the occasion.
The different sections of this article would explain
- What is VMWare?
- How to create VMImages?
- How to add hardware resources?
- What is a snapshot?
- Replicating the Environments
The sections contain very useful tips especially for adding resources. I faced difficulty in adding hard disks so I want to share my information with other people so that they do not have to re-invent the wheel.
What is VMWare?
VMWare is virtualisation software. In simple terms, VMWare Workstation allows one physical machine to run two or more operating systems simultaneously. The machine on which the Vmware software runs is called the Host Machine. Within this software you can create and run virtual operating systems known as VMImages. The figure below shows two Vmimages of Windows Server 2000 and Windows XP Pro being run on host Windows Server 2003 machine.
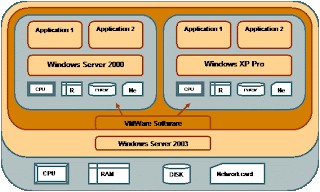
Fig 1:Two Vmwares running different applications on one host machine and using the h/w resources of the host machine
Creating VMImages:
After having a good understanding of the VMImages it is time to create one. There are two important parts of creating a VMImage
- VMDK files- This is virtual machine disk file. It encapsulates an entire server or desktop environment information. The vmdk file describes and documents the virtual machine environment and how it is stored. Click here for more info.
- VMX- This file is used for storing the configuration information about the VMImage.More information about Vmx files can be obtained from here.
Steps to create a new VmImage, using Vmware Workstation or VMware Server Console.
- Go to File New->Virtual Machine. It will open a wizard to guide you through the creation of VMImage.
- Select a guest operating system from the wizard screen
- Just give defaults for everything. It will take 8 GB as the default size of the disk. When you finish the wizard and press ok it will start creating the Disk File.
- Once the Disk File is created you need to create Vmx file by starting the Virtual machine you have saved in earlier steps.
- On starting the virtual machine the VMWare software will search for a bootable CD in the CD drive. Just insert the CD of the OS of which you have to create a VMImage. In my case I had to create a Japanese VMImage. So I inserted the CD of windows server 2003 Japanese.
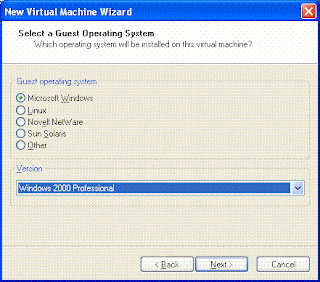
It is similar to normal OS Installation now
Like the guide, then subscribe by entering you mail id to get updates daily
Don't miss any article:Get it by E-mail
V-Model for Testing-A famous interview Question

Requirements analysis:In this phase, the requirements of the proposed system are collected by analyzing the needs of the user(s). This phase is concerned about establishing what the ideal system has to perform. However, it does not determine how the software will be designed or built. Usually, the users are interviewed and a document called the user requirements document is generated. The user requirements document will typically describe the system’s functional, physical, interface, performance, data, security requirements etc as expected by the user. It is one which the business analysts use to communicate their understanding of the system back to the users. The users carefully review this document as this document would serve as the guideline for the system designers in the system design phase. The user acceptance tests are designed in this phase.
System Design:System engineers analyze and understand the business of the proposed system by studying the user requirements document. They figure out possibilities and techniques by which the user requirements can be implemented. If any of the requirements are not feasible, the user is informed of the issue. A resolution is found and the user requirement document is edited accordingly.The software specification document which serves as a blueprint for the development phase is generated. This document contains the general system organization, menu structures, data structures etc. It may also hold example business scenarios, sample windows, reports for the better understanding. Other technical documentation like entity diagrams, data dictionary will also be produced in this phase. The documents for system testing is prepared in this phase.
Architecture Design:This phase can also be called as high-level design. The baseline in selecting the architecture is that it should realize all which typically consists of the list of modules, brief functionality of each module, their interface relationships, dependencies, database tables, architecture diagrams, technology details etc. The integration testing design is carried out in this phase.
Module Design:This phase can also be called as low-level design. The designed system is broken up in to smaller units or modules and each of them is explained so that the programmer can start coding directly. The low level design document or program specifications will contain a detailed functional logic of the module, in pseudocode - database tables, with all elements, including their type and size - all interface details with complete API references- all dependency issues- error message listings- complete input and outputs for a module. The unit test design is developed in this stage.
Don't miss any article:Get it by E-mail
Manual vs. Automated
Many large software organizations perform automated testing. Some have developed their own automated testing environments specifically for internal development, and not for resale.
Like the guide, then subscribe by entering you mail id to get updates daily
Don't miss any article:Get it by E-mail
20 Top Tips for Software Testing-Must listen Audio
Click here to listen:20 Top Tips for Software Testing
Like the guide, then subscribe by entering you mail id to get updates daily Don't miss any article:Get it by E-mail
Testing vs QA vs QC
Quality Control: A set of activities designed to evaluate a developed working product.
Quality Assurance: A set of activities designed to ensure that the development and/or maintenance process is adequate to ensure a system will meet its objectives.
The key difference to remember is that QA is interested in the process whereas testing and quality control are interested in the product. Having a testing component in your development process demonstrates a higher degree of quality (as in QA).
Like the guide, then subscribe by entering you mail id to get updates daily
Don't miss any article:Get it by E-mail
Funny Software Testing Terminology !
AGGRESSION TESTING: If this doesn't work, I'm gonna kill somebody.
COMPRESSION TESTING: []
CONFESSION TESTING: Okay, okay, I did program that bug.
CONGRESSIONAL TESTING: Are you now, or have you ever been a bug?
DEPRESSION TESTING: If this doesn't work, I'm gonna kill myself.
EGRESSION TESTING: Uh-oh, a bug... I'm outta here.
DIGRESSION TESTING: Well, it should work, but let me tell you about my truck...
EXPRESSION TESTING: #@%^&*!!!, a bug!
OBSESSION TESTING: I'll find this bug if it is the last thing that I do.
OPPRESSION TESTING: You will test this, now!
POISSION TESTING: Alors! Regardez le poission!
REPRESSION TESTING: It's not a bug, it's a feature.
SUCCESSION TESTING: The system is dead. Long live the new system!
SUGGESTION TESTING: Well, it works but wouldn't it be better if...
PRESIDENTIAL TESTING: Using the definition of testing as defined in the affidavit...
Like the guide, then subscribe by entering you mail id to get updates daily
Don't miss any article:Get it by E-mail
Who is a Good Developer ?
Like the guide, then subscribe by entering you mail id to get updates daily
Don't miss any article:Get it by E-mail
Think of it and Answer
ANSWER: Testers just report that it's dark.
Like the guide, then subscribe by entering you mail id to get updates daily
Don't miss any article:Get it by E-mail
Developers are not good testers. What you say?
The main concern of developer testing is - misunderstanding of requirements. If requirements are misunderstood by developer then no matter at what depth developer test the application, he will never find the error. The first place where the bug gets introduced will remain till end, as developer will see it as functionality.
Optimistic developers - Yes, I wrote the code and I am confident it’s working properly. No need to test this path, no need to test that path, as I know it’s working properly. And right here developers skip the bugs.
Developer vs Tester: Developer always wants to see his code working properly. So he will test it to check if it’s working correctly. But you know why tester will test the application? To make it fail in any way, and tester surely will test how application is not working correctly. This is the main difference in developer testing and tester testing.

This is all applicable to a developer who is a good tester! But most of the developers consider testing as painful job, even they know the system well, due to their negligence they tend to skip many testing paths, as it’s a very painful experience for them. If developers find any errors in their code in unit testing then it’s comparatively easier to fix, as the code is fresh to them, rather than getting the bug from testers after two-three days. But this only possible if the developer is interested in doing that much testing.
It’s testers responsibility to make sure each and every path is tested or not. Testers should ideally give importance to all small possible details to verify application is not breaking anywhere.
Developers, please don’t review your own code. Generally you will overlook the issues in your code. So give it to others for review.
Everyone is having specialization in particular subject. Developers generally think how to develop the application on the other hand testers think how the end user is going to use the application.
So in short there is no problem if developers are doing the basic unit testing and basic verification testing. Developers can test few exceptional conditions they know are critical and should not be missed. But there are some great testers out there. Through the build to test team. Don’t waste your time as well. For success of any project there should be independent testing team validating your applications. After all it’s our (testers) responsibility to make the ‘baby’ smarter!!
What you say? Comment here
Don't miss any article:Get it by E-mail